Lipid-based Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery
Since the discovery of insulin in 1921 and its clinical approval in 1982, therapeutic peptides and proteins have played a vital role in modern medicine. These biomolecules offer high target selectivity, well-defined mechanisms of action, and superior safety profiles compared to conventional small molecules. Advances in synthetic and recombinant technologies have further enhanced their therapeutic potential. However, their clinical application remains challenged by poor oral bioavailability, due to enzymatic degradation, low membrane permeability, and rapid renal clearance.
Parenteral administration is still the norm, but it is invasive and reduces patient compliance. As a result, non-invasive alternatives—particularly oral delivery—are increasingly sought after. Oral delivery offers convenience but is hindered by the gastrointestinal (GI) tract’s harsh environment, including acidic pH, peptidases, and poor epithelial permeability. Despite these obstacles, several oral peptide/protein formulations have reached clinical development, driven by innovative drug delivery technologies.
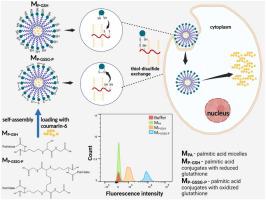
Lipid-based nanocarriers—such as oil-in-water nanoemulsions, self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS), solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs), liposomes, and micelles—are emerging as promising tools for oral delivery. They protect encapsulated peptides from degradation, facilitate mucus penetration, and enhance cellular uptake through mechanisms like endocytosis, transcytosis, and membrane fusion. These carriers can also be paired with permeation enhancers such as bile salts and fatty acids to further improve absorption.
A key strategy in enabling lipophilic formulation of hydrophilic macromolecules is hydrophobic ion pairing (HIP). HIP involves non-covalent complexation of ionizable biomolecules (e.g., peptides, proteins, nucleic acids) with hydrophobic counterions, reducing aqueous solubility and enhancing lipid compatibility. Electrostatic interactions—often using biocompatible surfactants like sulfonates and phosphates—are central to HIP. For example, insulin paired with sodium deoxycholate has shown improved oral bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy in preclinical models.
Reverse micelles (RMs) offer a complementary strategy. Dry RMs, formed through lyophilization or solvent evaporation, encapsulate hydrophilic drugs in a lipid-compatible structure, further protecting them from degradation and enhancing lipophilicity. In summary, the combination of HIP or RMs and lipid-based nanocarriers offers a powerful platform for oral delivery of peptides and proteins, overcoming key biological barriers and enabling formulation versatility. These technologies are poised to transform the landscape of non-invasive biopharmaceutical delivery.
Latest publications:
References
- Sandmeier M, Ricci F, To D, Lindner S, Stengel D, Schifferle M, Koz S, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Design of self-emulsifying oral delivery systems for semaglutide: reverse micelles versus hydrophobic ion pairs. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jun;15(6):2146-2161. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01729-0
- Claus V, Sandmeier M, Hock N, Spleis H, Lindner S, Kalb M, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Counterion optimization for hydrophobic ion pairing (HIP): Unraveling the key factors. Int J Pharm. 2023 Nov 25;647:123507. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123507
- Jörgensen AM, Steinbring C, Stengel D, To D, Schmid P, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS) Containing Reverse Micelles: Advanced Oral Formulations for Therapeutic Peptides. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Dec;12(31):e2302034. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302034
- Haddadzadegan S, Dorkoosh F, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Oral delivery of therapeutic peptides and proteins: Technology landscape of lipid-based nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Mar;182:114097. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114097
- Ismail R, Phan TNQ, Laffleur F, Csóka I, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Hydrophobic ion pairing of a GLP-1 analogue for incorporating into lipid nanocarriers designed for oral delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020 Jul;152:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.04.025
- Phan TNQ, Shahzadi I, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Hydrophobic ion-pairs and lipid-based nanocarrier systems: The perfect match for delivery of BCS class 3 drugs. J Control Release. 2019 Jun 28;304:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.05.011