Charge-converting Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery
Over the past 20 years, surface charge-reversible nanoparticles (NPs) have emerged as a promising strategy to address the “polycation dilemma” in drug and gene delivery. This dilemma stems from the opposing requirements for nanoparticle surface charge: while negatively charged or neutral NPs are ideal for systemic circulation due to reduced interactions with serum proteins and extracellular barriers, positively charged NPs are better suited for cellular uptake and intracellular delivery. Charge-reversible NPs reconcile this by starting with a neutral or negative charge and switching to a positive charge in response to specific stimuli at the target site.
These stimuli—such as changes in pH, redox environment, enzyme presence, or external triggers (e.g., heat, light)—induce a surface charge conversion that enhances NP interactions with negatively charged cellular membranes. This transformation improves cellular adhesion, uptake, endosomal escape, and even mitochondrial targeting, thereby increasing therapeutic and diagnostic efficacy. Additionally, these NPs can penetrate bacterial biofilms and deliver antibiotics directly to pathogens.
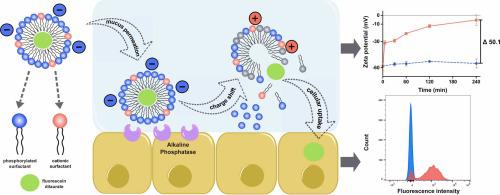
Charge conversion is typically achieved by incorporating functional groups or coatings that respond to environmental cues. During circulation, neutral or mildly anionic NPs (zeta potentials between –30 and 0 mV) maintain high mobility and stability, avoiding premature opsonization and clearance. Upon reaching acidic environments—like tumor tissues or endosomes—they convert to a cationic state, promoting strong electrostatic interactions with target cells.
Positively charged NPs, if administered directly, are rapidly cleared due to nonspecific binding with serum proteins. Charge-reversible systems overcome this by delaying activation until they reach the intended site, thereby maximizing efficacy while minimizing systemic side effects.
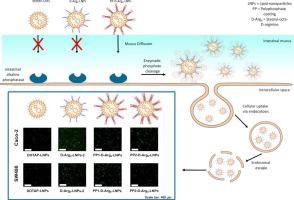
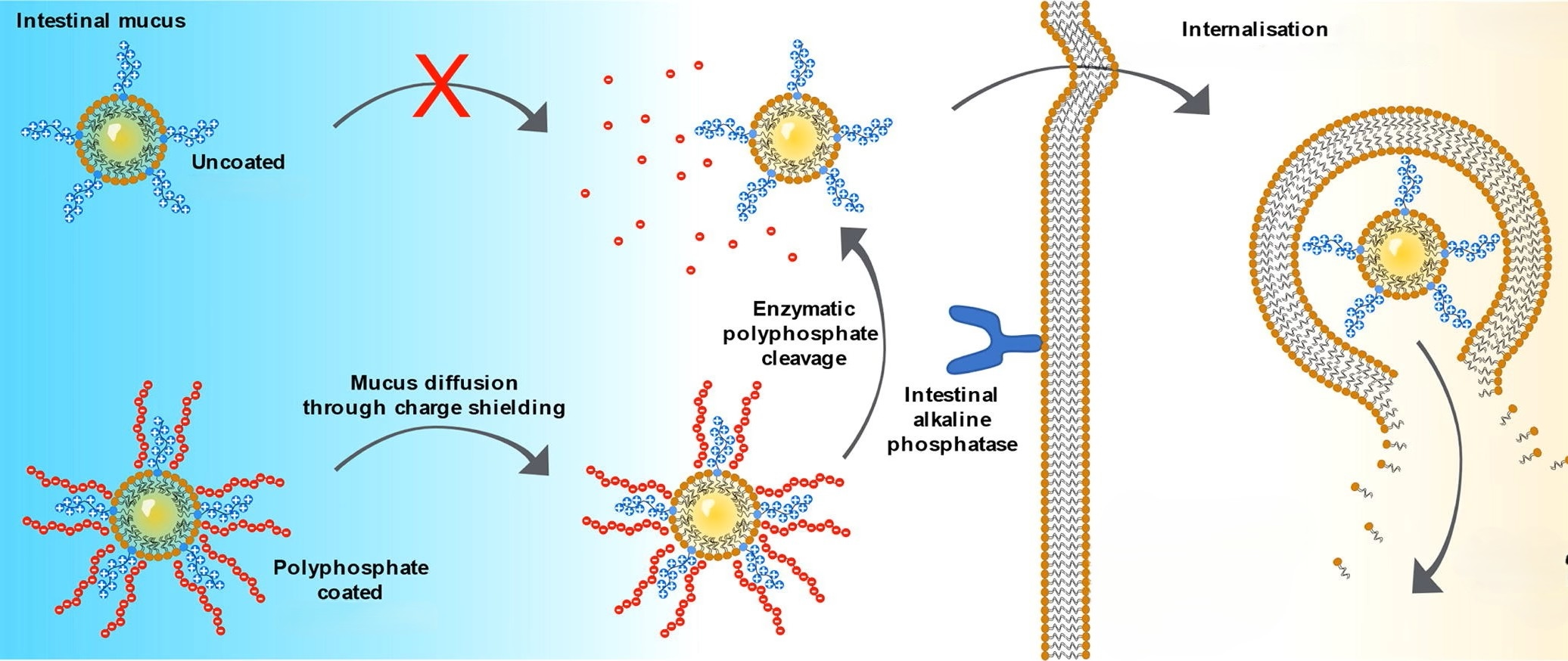
This technology also shows particular promise in mucosal delivery, including intestinal, pulmonary, and ocular applications. Negatively charged NPs cross mucus barriers efficiently, then convert to a positive charge to facilitate epithelial uptake.
In gene delivery, alkaline phosphatase (ALP)-triggered charge-reversal NPs have shown selective transfection of cell lines such as Caco-2 and HEK-293. In cystic fibrosis models, negatively charged NPs penetrated thick mucus layers and, after ALP activation, outperformed Lipofectamine in delivering CFTR plasmid DNA. Modified lipid-based carriers further enhanced pDNA delivery by 7.2-fold post-conversion.
Overall, charge-reversible nanoparticles offer a dynamic and targeted approach to overcome physiological barriers, enhancing both drug and gene delivery systems.
Latest publications:
References
- Veider F, Sanchez Armengol E, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Charge-Reversible Nanoparticles: Advanced Delivery Systems for Therapy and Diagnosis. Small. 2024 Jan;20(3):e2304713. doi: 10.1002/smll.202304713
- Saleh A, Stengel D, Truszkowska M, Blanco Massani M, Kali G, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Nanostructured lipid carriers decorated with polyphosphate coated linear and loop cell-penetrating peptides. Int J Pharm. 2024 Dec 25;667(Pt A):124844. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124844
- Zöller K, Haddadzadegan S, Lindner S, Veider F, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Design of charge converting lipid nanoparticles via a microfluidic coating technique. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Nov;14(11):3173-3185. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01538-5
- Veider F, Zöller K, Saleh A, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Overcoming intestinal barriers by heparanase-responsive charge-converting nanocarriers. Int J Pharm. 2024 Feb 15;651:123817. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.123817
- Nguyen Le NM, Zsák S, Le-Vinh B, Friedl JD, Kali G, Knoll P, Seitter HW, Koschak A, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Charge-Converting Nanoemulsions as Promising Retinal Drug and Gene Delivery Systems. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Oct 5;14(39):44981-44991. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c11649
- Efiana NA, Fürst A, Saleh A, Shahzadi I, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Phosphate decorated lipid-based nanocarriers providing a prolonged mucosal residence time. Int J Pharm. 2022 Sep 25;625:122096. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122096
- Knoll P, Hörmann N, Nguyen Le NM, Wibel R, Gust R, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Charge converting nanostructured lipid carriers containing a cell-penetrating peptide for enhanced cellular uptake. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Dec 15;628(Pt A):463-475. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.07.160
- Kali G, Knoll P, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Emerging technologies to increase gastrointestinal transit times of drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2022 Jun;346:289-299. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.016
- Federer C, Claus V, Hock N, David Friedl J, Wibel R, Bernkop-Schnürch A. Charge-reversal nanoemulsions: A systematic investigation of phosphorylated PEG-based surfactants. Int J Pharm. 2022 Feb 5;613:121438. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121438
- Bernkop-Schnürch A. Strategies to overcome the polycation dilemma in drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018 Nov-Dec;136-137:62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.07.017